Guiliani:Features: Difference between revisions
From Guiliani
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Overview == | |||
Guiliani is a C++ software framework enabling the creation of visually appealing, hardware and OS platform independent GUIs for embedded systems. | Guiliani is a C++ software framework enabling the creation of visually appealing, hardware and OS platform independent GUIs for embedded systems. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Minimum HW requirements == | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Criteria | !Criteria | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
== Architecture overview == | |||
Guiliani is split into two layers, the Guiliani runtime-engine and a platform abstraction layer. | Guiliani is split into two layers, the Guiliani runtime-engine and a platform abstraction layer. | ||
[[File:Architecture 20.jpg]] | [[File:Architecture 20.jpg]] | ||
== Features == | |||
=== System, platform and periphals === | |||
* Object-oriented GUI framework for embedded systems using C++ | * Object-oriented GUI framework for embedded systems using C++ | ||
* Optimized for embedded devices | * Optimized for embedded devices | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
=== GUI features === | |||
* Large set of pre-defined widgets | * Large set of pre-defined widgets | ||
* Easy to customize existing widgets or to integrate new widgets | * Easy to customize existing widgets or to integrate new widgets | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
=== Application development & support === | |||
* Comprehensive and up-to-date documentation | * Comprehensive and up-to-date documentation | ||
* Customizable trainings regarding content, location and time | * Customizable trainings regarding content, location and time | ||
Revision as of 10:24, 13 January 2017
Overview
Guiliani is a C++ software framework enabling the creation of visually appealing, hardware and OS platform independent GUIs for embedded systems.
Guiliani adopts the philosophy of write once, compile for & run on many different target hardware. Once a Guiliani application has been developed, it can run natively on supported target platforms. When using Guiliani, the usual development workflow is to design the application on a PC and target a set of embedded operating systems for production release.
Minimum HW requirements
| Criteria | Requirements |
|---|---|
| MCU | 100Mhz |
| ROM | ~700kb for Guiliani without resources |
| RAM | ~50kb for Guiliani without resources |
| Compiler | C++ Compiler with exception Support |
| Operating System | “bare-metal”, many OSs supported |
Architecture overview
Guiliani is split into two layers, the Guiliani runtime-engine and a platform abstraction layer.
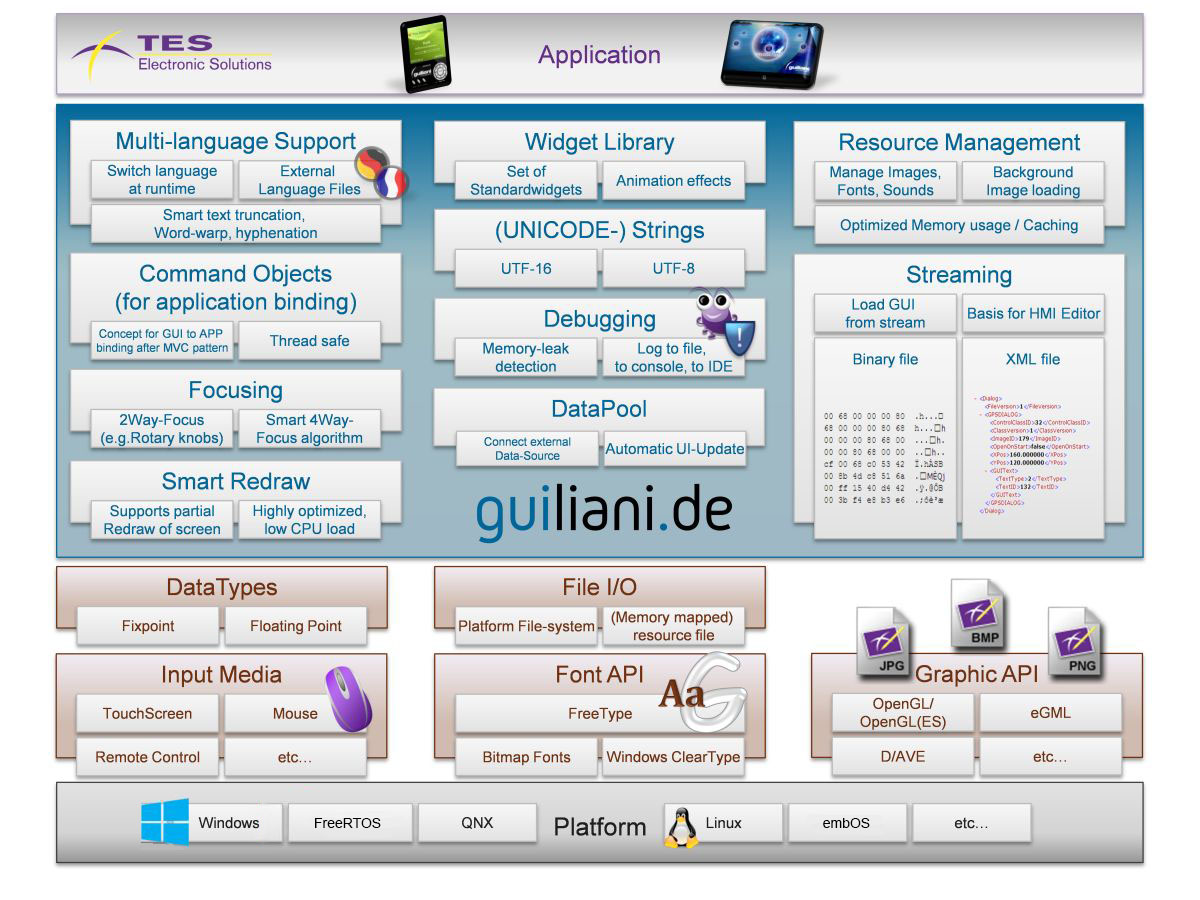
Features
System, platform and periphals
- Object-oriented GUI framework for embedded systems using C++
- Optimized for embedded devices
- Low memory consumption
- Minimized CPU usage
- Operation system independent
- CPU independent
- Support for fixpoint / floating point CPUs
- So far supported embedded platforms include: Renesas RZ/A, RZ/G, SH2, RX600, ST STM32F429, ALTERA NIOS II, Intel x86,…
- Independent of graphics/font engine
- Supports all types of input media
- Support for subpixel-accurate rendering
- Support for hardware-specific capabilities (e.g. hardware graphic layers)
- UNICODE support
- Prepared for thread-safe integration into existing applications
GUI features
- Large set of pre-defined widgets
- Easy to customize existing widgets or to integrate new widgets
- Support for animations
- Multi-language support (dynamically switchable at runtime)
- Image-sets (skinning)
- Automated layout of GUI elements
- Rich-text support
- Smart redraw mechanism and resource-management
- GUI can be developed independently from applications
Application development & support
- Comprehensive and up-to-date documentation
- Customizable trainings regarding content, location and time
- Tutorials available
- Integrated debugging mechanism
- GUI design and behavior is stored in XML or binary description-files
- Easy communication with external applications